Near Field Communication (NFC) is used to instill objects, places, or people with digital information. A scanner is used to read the information stored in the NFC tag over a distance of a few centimeters. The most common use for NFC is the identification of an object, a person or a place.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) leverages the possibilities of Bluetooth in a very energy-saving manner for data transmission over a maximum of several hundred meters. Frequent uses for BLE are the identification of locations from a distance (e.g. bus stops from a bus), and the checking of inventory in larger areas (e.g. on a construction site).
With LoRa, data can be transmitted over a few kilometers without a SIM card, and requires very little power. Despite the long range, LoRa devices can operate autonomously for several years without needing battery changes. A typical use of LoRa is for the transmission of sensor data or machine data within a city or within a company site.
NFC (Near Field Communication) Technology allows you to send data over radio waves and is used to instill objects, places, or people with digital information.
Scanning NFC tags sends the information stored in the NFC tag over a distance of a few centimeters. This requires only an NFC-enabled smartphone as well as an NFC tag.
In most of our customers’ applications, no information is stored in the NFC tag other than the globally unique number of each tag. Instead, the unique NFC tag number is used to load the associated data from the ginstr cloud as needed. The advantage: the data associated with the NFC tag can be changed without going to the NFC tag.
Any data can be assigned to each tag, e.g. information about a machine (type, tenant, person responsible, etc.), information about an employee (working hours, team membership, authorisations, etc.) or information about a location (e.g. for security guards).

Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is an indoor and outdoor identification and localisation technology that uses small wireless tags called “iBeacons”, to communicate with your smartphone.
These beacons are small Bluetooth emitters that have low energy consumption and their batteries generally last for several years.
ginstr apps can receive data from any number of iBeacons to identify locations (e.g. a bus stop, a supermarket shelf, etc.).
Beacons can also be used to identify the exact location of an employee (e.g. within a hospital, airport, mine or tunnel, or outside on a construction site or campsite).
For this, several of these very cost-effective beacons can be mounted across the facility, and then with the so-called ‘fingerprint’ technology the location of the smartphone (and its user) can be determined. This is especially useful in cases where GPS either does not work (e.g. inside buildings), or requires too much power.

LoRa is a long-range network technology for low-speed communication of connected objects. Like BLE, the LoRa protocol allows both indoor and outdoor data transmission over long distances (3 to 10km).
LoRa consumes less power and is more cost-efficient than any other traditional mobile network, which allows you to remotely monitor distant objects for several years with only one battery.
Unlike mobile phones that are always switched on and keep consuming without interruption, LoRa equipment is not permanently accessible. It activates periodically and takes advantage of its “awakening” to check if there is new information to be recorded and issue an alert when necessary. GSM technology offers the same service but comes with higher costs.
To deploy this network, it is necessary to use (gateways) antennas. It also acts as routers and transmitters for the wireless network.


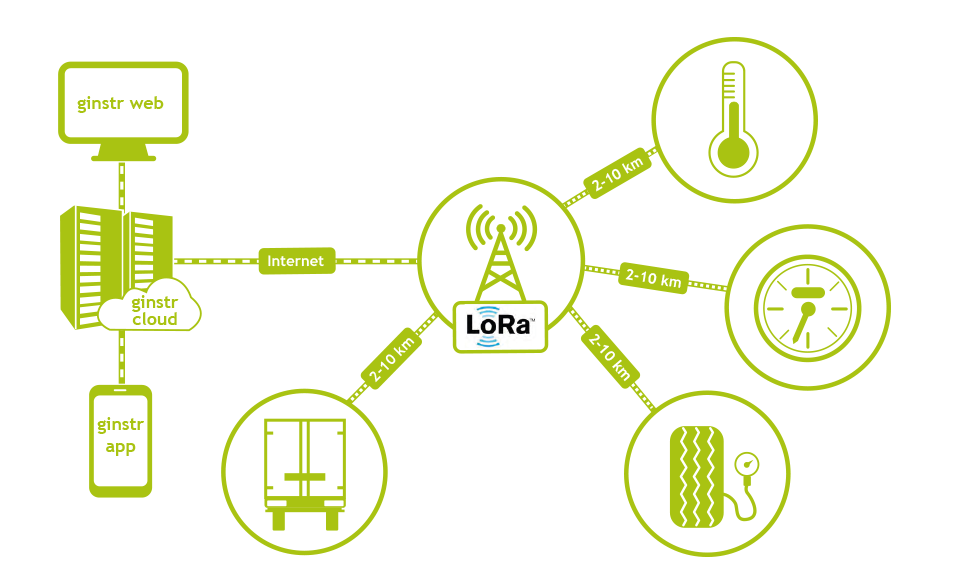
Wireless remote sensing (e.g. for tire pressure; temperature in truck compartments,; temperature in transport boxes for blood tests, drugs, organs, etc.; status of container doors and equipment in containers; operating hours of machines; energy consumption of heating systems, cooling systems, cleaning machines; electricity, water and gas counters; etc.).
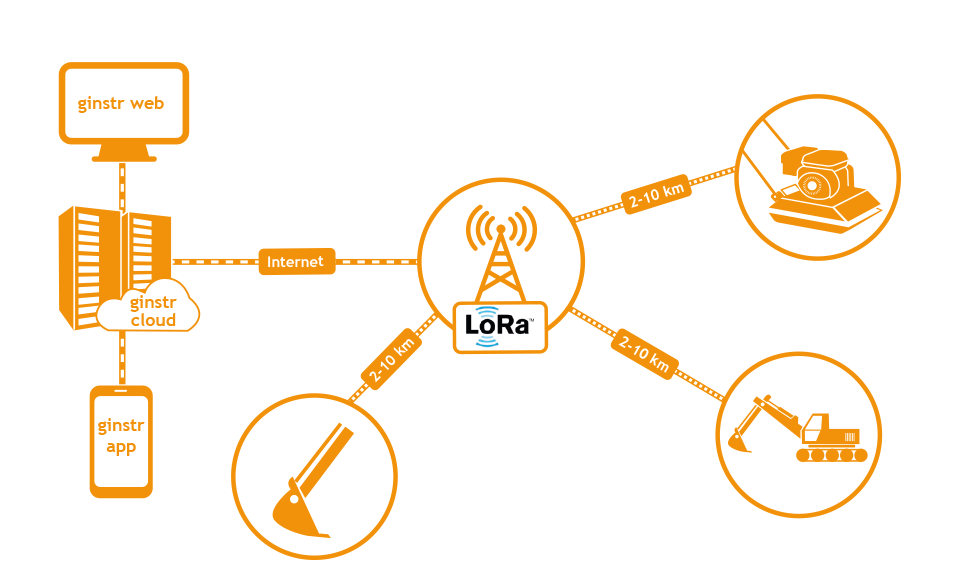
Automated registration of presence/absence of assets on construction sites, in mines, etc. (e.g. construction machinery accessory equipment such as excavator shovels, expensive drilling machines, tool boxes etc.)
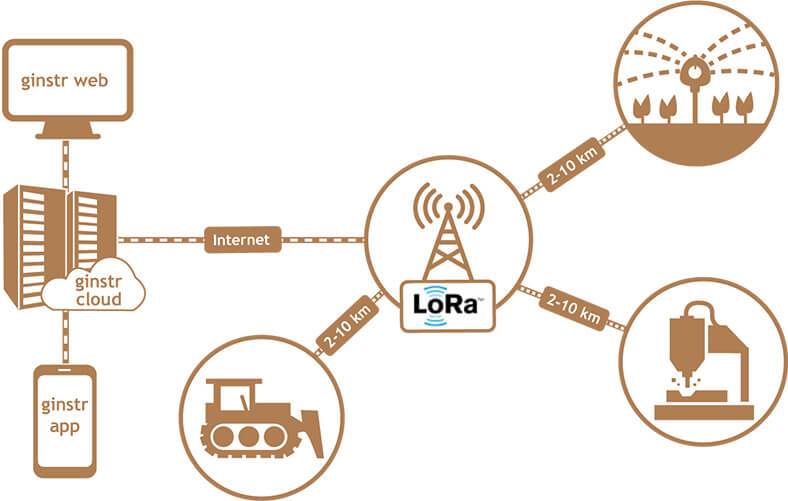
Wireless remote control (e.g. immobilisation of construction machinery, activation/deactivation of sprinklers watering the fields, etc.)